An organization with poor data quality issues can take the first step to resolving them by conducting data auditing. Organizations rely on this process to safeguard data, comply with regulations, and make informed decisions.
In this article, we’ll examine the value of data auditing and discuss how to do it effectively.
Data Auditing Best Practices: Table of Contents
What is Data Auditing and What are Its Advantages
Data auditing is the process of analyzing and reviewing the state of enterprise data to guarantee optimal utility & security. The objective is to detect errors, risks, or anomalies and correct them as soon as possible.
Ideally, a data audit should be conducted at least once a year to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and security. During this period, analysts and stakeholders work together to examine how the organization gathers, stores, and leverages data.
The benefits of data auditing include:
- Improved security posture. Data audits reveal vulnerabilities and weaknesses of an organization’s IT infrastructure. Specifically, this audits allow for security controls to be improved and the risk of data loss and security breaches reduced.
- Monitored access controls. Data audits review user permissions across the entire IT network, as a matter of fact, they limit exposure to unauthorized users and prevent insider threats.
- Regulatory Compliance Assurance. Data audits enable organizations to maintain compliance with constantly changing legislation at the local, state and federal levels.
- Increased trust and utility of enterprise data. Data audits improve enterprise data integrity/quality. As a result, they enable organizations to broaden leverage of data as an asset and maximize the function of enterprise data management tools to simplify modern data landscapes.
- Enhanced efficiency and decision-making. Data audits help organizations understand how their business processes impact reporting abilities. It also identifies and improves quality issues that influence operations and decision-making.
- Simplified data integrations. Data audits help organizations create better data strategies as they continue to acquire and integrate additional data through mergers and acquisitions.
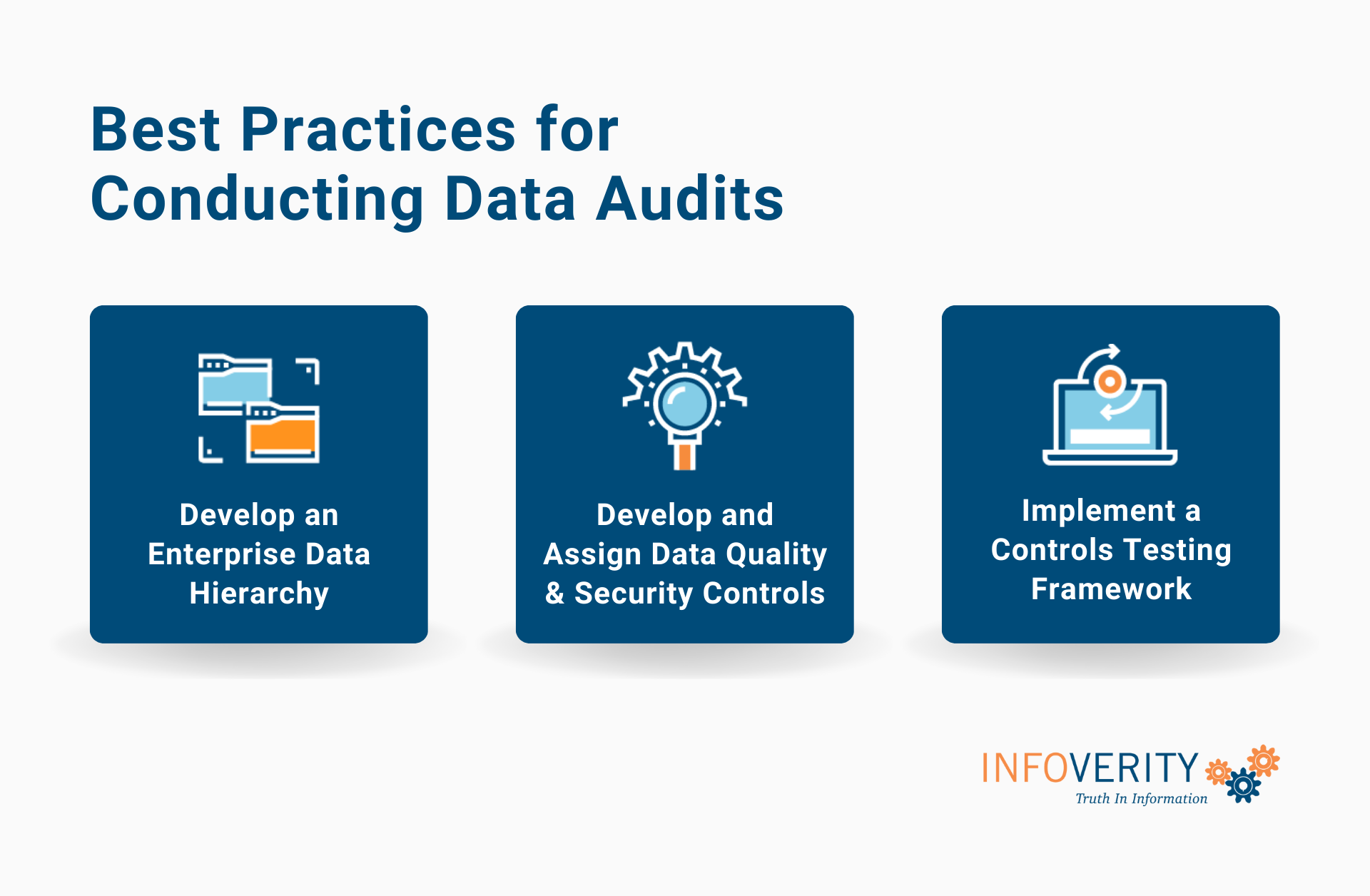
Three Best Practices for Conducting Data Audits
The following practices can help companies improve their data auditing process, enhance data quality & security, and maintain data governance.
Develop an Enterprise Data Hierarchy
Data hierarchies serve to organize data elements in a tree-like format. Specifically, each level reveals more information and gets more specific, giving organizations an easier way to understand and analyze data at different enterprise layers.
For instance, in healthcare, a data hierarchy can start with the entire organization, drop down to the department level, then to the service level, and finally to the patient level.
The data hierarchy is crucial to data audits, as laying out domains and sub-domains by business area ensures that an up-to-date data inventory is available. Many enterprises produce too much data that can easily get out of control. Therefore, compiling an overview of the data landscape should be the first order of business.
Develop and Assign Data Quality & Security Controls
Measuring enterprise data quality and security risks isn’t straightforward, because organizations are rarely able to identify a single source of truth to compare standards against.
Prior to auditing data, organizations need to identify data quality and security controls for domains within the hierarchy. Controls refer to the methods, rules, and standards used to ensure the quality and security of data. Examples include data access restrictions, validation rules, and error monitoring.
In addition, these controls should focus on all existing data domains (customer data, product data, and employee data) and their corresponding hierarchy levels (from high-level summary down to detailed transactions).
Example
A good example would be the hierarchy of customer transaction details within the customer data domain. Among the controls a retail company can implement are ensuring all customer records contain accurate contact information, no duplicates, and regularly updated privacy and consent preferences.
Implement a Controls Testing Framework
Internal controls testing speeds up and standardizes the audit process. The primary objective is to determine if internal controls are effective in preventing quality errors or security risks. Additionally, testing yields the assurance necessary for demonstrating compliance. Especially in situations where individual substantive procedures may not suffice.
Furthermore, controls should be documented in a comprehensive control testing framework. Having a detailed framework library allows organizations to tie out data quality thresholds and potential security risks to the most critical system areas.
Testing scope and frequency can vary by individual control. Sometimes this means testing the entire control population, while other times it means reviewing a representative sample. In either case, high-impact controls and/or those that have failed previous tests should be revisited and tested more often.
Over time, companies will need to revisit and adapt controls testing framework to evolving legislation and business landscape changes.
The Relationship Between Data Auditing and Data Governance
Data auditing is a data management function that helps identify any data-related issues, risks, or errors, that could negatively impact organizations in making well-informed decisions and formulating effective business strategies.
On the other hand, data governance functions as a strategic center of excellence that unifies individual data management activities (including data auditing).
The relationship between the two is intrinsic and symbiotic, each contributing to effective Enterprise Data Management.
Companies can’t get a full picture of their data landscape without data audits. This lack of insight poses challenges when implementing effective data governance strategies. At the same time, data audits are also necessary to establish assurance, trust, and proof of effective data governance.
Therefore, a well enabled data governance entity should be involved in creating, implementing, and managing the data auditing function. It is their responsibility to safeguard the integrity of the data lifecycle and data output, as well as to enforce policies to enhance security and comply with regulations.
Data Audits Are Critical For Enterprise Data Modernization
Emerging data initiatives, such as the integration of AI/ML tools, are at the forefront of many industry sectors. Now more than ever, Data Auditing continues to be a vital part of managing and overseeing the integrity, security, and operability of data in this dynamic digital age.
To make sure your data quality, privacy/security and IT infrastructure can cope, conduct comprehensive data audits regularly and update your data governance practices accordingly. Infoverity can assist you in this regard. Contact us today.
FAQ – Data auditing
What is data auditing?
Data auditing is the process of analyzing and reviewing the state of enterprise data to guarantee optimal utility & security. The objective is to detect errors, risks, or anomalies and correct them as soon as possible.
How to conduct a data audit?
Measuring enterprise data quality and security risks isn’t straightforward, because organizations are rarely able to identify a single source of truth to compare standards against. Prior to auditing data, organizations need to identify data quality and security controls for domains within the hierarchy.
What are the benefits of data auditing?
Data auditing improves security, ensures compliance, and enhances data quality for better decision-making. It helps monitor access controls, strengthens data integrity, and simplifies integration as businesses grow. Regular audits reduce risks, optimize operations, and maximize the value of enterprise data.
How to audit data governance?
The relationship between Data Auditing and Data Governance is intrinsic and symbiotic, each contributing to effective Enterprise Data Management. Companies can’t get a full picture of their data landscape without data audits. This lack of insight poses challenges when implementing effective data governance strategies.
Download The Guide
Looking for a guide to deploy non-invasive data governance across your organization?
Download our free white paper and discover how to implement data governance seamlessly at your company.