Enterprises thrive when they’re able to derive useful business insights from collected data. However, making sense of the data they maintain can be challenging, as not all collected data is in a state where it can be usable, helpful, or relevant. Data integration best practices provide a viable solution. Streamlined data reveals what’s essential, paving the way for better business workflows and innovative solutions that drive success.
Quite often, the key to successful integrations lies in selecting the right tools to handle growing data volumes associated with modern data management practices. However, choosing the right one can create additional challenges for many enterprises.
In this article, we focus on these issues, as well as how to help narrow down the search to determine which tools are best suited for various organizations.
No time to read?
Listen on the go — skip the scroll and absorb the insights hands-free. This post is part of Infoverity’s Audio Blog Archive — built for busy professionals like you.
Finding The Right Data Integration Tool: Table of Contents
Why Is It Difficult to Select the Right Data Integration Tools?
The market offers a myriad of options for data integration tools, leaving organizations struggling to decide on the best option to implement. Decision-makers, often IT managers, chief data officers, and other senior executives, find it particularly challenging due to:
Complexity of Requirements
Each data integration tool comes with different features, capabilities, and levels of customization. Enterprises need to match these to their specific needs.
Example
A large hospital with a wide variety of patient data sources must select a tool that is capable of handling multiple data types (ex: medical images, lab results, and EHA). The tool should also conform to healthcare regulations such as HIPAA and offer customization to fit the hospital’s unique workflows.
These complex requirements make it difficult to find a solution that meets all of them.
Compatibility with Existing Systems
Data integration tools should work seamlessly with the organization’s existing systems and those planned or anticipated in the future.
A data integration tool for manufacturers, for instance, must connect various systems, from supply chain management to production control systems, ensuring real-time data flow to avoid bottlenecks and maintain efficiency.
Any misalignment can lead to significant operational challenges, complicating the selection process.
Scalability
A proper data integration tool should have the capacity to grow at scale with the organization, adapting to any changes.
For example, retail companies must manage increasing data volumes from various sources, including online transactions, inventory management, and customer relationships. As the business expands, an integration tool should be able to support larger data sets and more complex integration scenarios without compromising performance.
Cost Considerations
The cost of data integration tools influences decisions significantly. Organizations must maintain a balance between their budget and the requirement for advanced features and scalability.
Decision-makers will need to evaluate the total cost of ownership. This includes setup costs, licensing fees, maintenance, and hiring experts or training staff.
Technical Expertise
The level of technical expertise available within the organization plays another key role in selecting a data integration tool.
Sources such as transaction records, market data, and customer information may require highly specialized tools. An institution without in-house technical expertise may prefer a user-friendly tool accompanied by reliable vendor support, even if it means foregoing some advanced features.
Looking for data integration guidance?
Infoverity can help your business derive useful business insights from collected data. To discover more on how we can help you achieve data management success while selecting the right data integration tool. Contact our team of experts today.
How To Select the Right Data Integration Tools
Choosing a data integration tool is a critical decision for any organization striving to harness the power of enterprise data. With countless options in the market, the decision-making process can quickly become overwhelming. This section provides a step-by-step guide to ensure your organization selects a tool that not only meets current business needs but is also equipped to scale with future requirements.
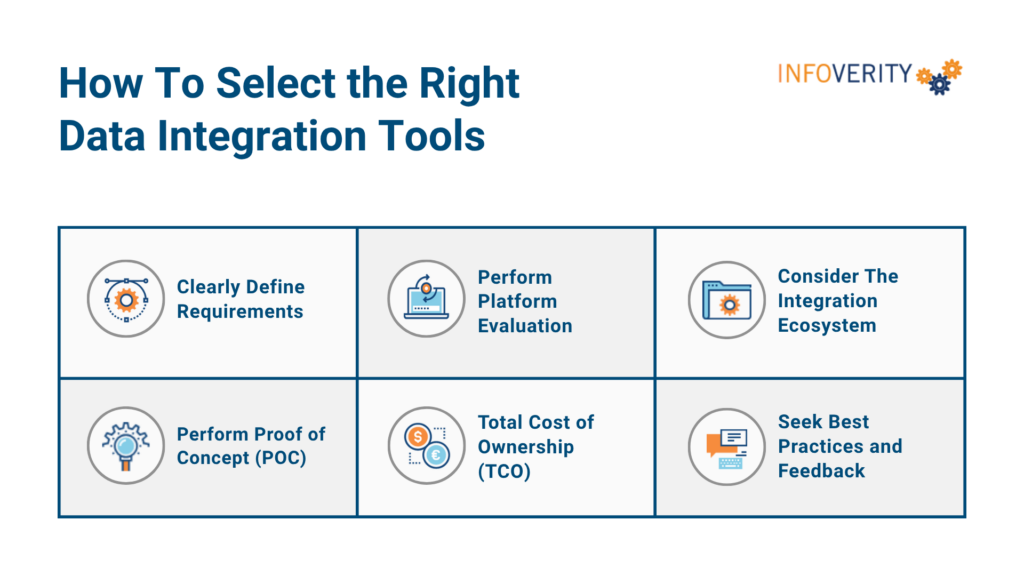
1. Clearly Define Requirements
Organizations require an inventory of all internal and external data sources intended for integration, including databases, APIs, file systems, and cloud services. These sources inform how a tool connects to and manages an organization’s various data streams.
Furthermore, the types of integration patterns must match the intended operational needs. Batch processing, for example, enables scheduled processing of large volumes of data. Conversely, real-time integration allows for data to be updated point-in-time. Understanding integration patterns is critical for ensuring the tool meets your specific processing and data flow needs.
As organizations evolve, their requirements and goals change as well. Defining scalability requirements is key to handling data volume growth and increased user demand.
Privacy and regulatory considerations should be a focus as well. Defining security requirements, such as encryption standards, access controls, and data masking, remains critical to protecting sensitive information. Understanding regulatory requirements for, such as GDPR and HIPAA, ensures that selected tools will adequately meet compliance needs.
2. Perform A Thorough Platform Evaluation
Different tools offer a range of features and functionalities, such as data transformation capabilities, connectivity options, and automation features. Matching these features to the organization’s needs ensures that the selected tool can handle enterprise specific data integration tasks efficiently. Additionally, each tool should be assessed for its ability to scale both vertically and horizontally.
Ease-of-use and overall user experience should be considered from the perspective of those who will be operating the tool day-to-day. An intuitive user interface can reduce training time and generally increase overall productivity.
Challenges and roadblocks are inevitable when implementing, operating and scaling tools. Often times, quick and timely support can be a make or break when recognizing value. A thorough review of vendor support capabilities, such as customer service channels, detailed documentation, and an active user community, will help guarantee continuous assistance and problem-solving resources are available to resolve issues timely.
3. Consider The Integration Ecosystem
An organization needs to ensure tools are compatible with existing systems, databases, applications, and cloud environments as seamless integration maximizes efficiency and leverages infrastructure investments currently in place.
Interoperability with data governance, data quality, and data cataloging systems play a large role in maximizing data management capabilities and automation. Understanding vendor offerings around prebuilt connectors and APIs is essential for reducing implementation time and complexity.
4. Perform Proof of Concept (POC)
Conducting a proof of concept (POC) can help evaluate data integration tools’ applicability in a real-world scenario and evaluate suitability and performance with minimal investment risk.
POC’s allow for organizations to outline and adjust goals and success criteria to ensure the tool meets enterprise specific needs. For example, insurance companies might start by selecting representative data sets involving claims processing and customer data integration. Based upon success measures in both areas, they can then prioritize roadmap next steps in either direction.
Configuring the tool in a controlled environment that mimics production setup allows for realistic testing while monitoring it against predefined metrics helps evaluate its scalability, performance, and user-friendliness.
Involving key business stakeholders, (ex: claims adjusters and business analysts for insurance companies), ensures the tool aligns with organizational needs.
5. Factor in Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Upfront costs become a large focal point during the tool selection process. However, considerations around the ongoing costs of maintenance, support, and training should not be overlooked. Here’s the breakdown:
- Upfront Costs: Initial costs, including software licenses, hardware, and implementation fees.
- Ongoing Costs: Recurring expenses such as subscription fees, maintenance, and support contracts.
- Training and Development: Cost of staff training and internal expertise development.
- Operational Costs: Costs of using and managing the tool, such as administrative costs.
- Upgrade and Scalability Costs: Potential future expenses, such as adding new features or users.
- Risk Mitigation: Allowance for costs associated with mitigating risks, such as data breaches and compliance issues.
A comprehensive TCO analysis supports informed decisions by providing a full understanding of the financial implications and long-term commitment.
6. Seek Best Practices and Feedback
Industry reports, analyst reviews, and technology reviews (Think: G2 and Capterra) are non-biased resources companies can reference when making decisions around integration tools. These sources often compare features, performance metrics, and user experiences. Seeking out first-hand accounts from professionals and industry peers can also provide insight into practical usage and related challenges.
Finally, vendors themselves can be a vital source of information. Vendor websites typically contain volumes of success stories and case studies illustrating how their solution has helped various organizations achieve success. Additionally, many vendors are willing to connect potential customers to current users should they need direct feedback or testimonials.
Finding the Right Tool and Getting the Right Help
Organizations can achieve data management success by following these strategies for selecting the right data integration tool. If your organization requires additional guidance, contact Infoverity today. Our team can help you make informed and strategic decisions, as well as assist with the implementation process.
FAQ – Data integration tools
What is a data integration tool?
Enterprises thrive when they’re able to derive useful business insights from collected data. However, making sense of the data they maintain can be challenging, as not all collected data is in a state where it can be usable, helpful, or relevant. Data integration best practices provide a viable solution.
How to select the right data integration tools?
Choosing the right data integration tool starts with clearly defining your organization’s requirements. Define your needs, assess tool features and compatibility, test with a proof of concept, and consider total cost of ownership. Use reviews and vendor insights to support your decision.
Why is it difficult to select the right data integration tools?
The market offers a myriad of options for data integration tools, leaving organizations struggling to decide on the best option to implement. Decision-makers, often IT managers, chief data officers, and other senior executives, find it particularly challenging.
What is an example of data integration tool?
Different tools offer a range of features and functionalities, such as data transformation capabilities, connectivity options, and automation features. Matching these features to the organization’s needs ensures that the selected tool can handle enterprise specific data integration tasks efficiently.